The Aluminum Alloy Die Casting Surface Defects and Solutions Part 1
Abstract: Summary of main causes for surface defects of cast alloy die casting: undercosting, cold shut, peeling, bubbles, flyer, slag inclusion, porosity, strain, hot cracking, hot brittleness, depression, expansion cracking, deformation, mucous membrane, shrinkage cavity, cracking, leakage, interlayer, impurities, flow marks, blistering, cracking
Summary of main causes for surface defects of aluminum alloy die casting:
1. The metal pressure is too low (low injection ratio);
2. The metal pressure is too high;
3. The first stage speed is too low;
4. The first stage speed is too high;
5. The first/second level switching point is too early;
6. The switching point of the first/second level is too late;
7. Deceleration setting error;
8. The second stage speed is too low;
9. The second stage speed is too high;
10. Pressurize too early;
11. The pressurization is too late;
12. The pressurization is too low;
13. The pressurization is too high;
14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly;
15. Blocked at the injection port;
16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace;
17. Blocking of the pipe of the dosing furnace;
18. Setting time is too long/short;
19. The clamping machine/guide post is not good;
20. The jacking force is too high;
21. Ejection delay is too short;
22. Ejection delay is too long;
23. The clamping force is too low/the machine tonnage is too small;
24. Operation cycle is irregular;
25. The mold has water/water pipe leakage;
26. The heating/cooling device leaks oil;
27. Too much punch lubricating oil;
28. The punch lubricant is insufficient/the punch is stuck;
29. The mold is too cold;
30. The mold is too hot;
31. Too much mold spraying;
32. Insufficient mold spraying;
33. Wrong mold spraying type;
34. The concentration of release agent is too low;
35. Dirty mold surface/metal adhesion;
36. Vacuum leakage;
37. The vacuum is opened too early/late;
38. Exhaust duct and/or overflow port fail;
39. Poor surface polishing of mold/injection cylinder;
40. Insufficient draft surface slope or side concave;
41. Poor design of ingate and runner;
42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points;
43. The geometric shape of the casting is difficult to form;
44. The metal is too hot/cold;
45. Metal is polluted or dirty;
46. The metal specification is incorrect;
47. There is scum in the molten material in the furnace.
Defect analysis of die castings
1、 Insufficient filling
Main features: the metal has been cooled and solidified before filling the mold cavity, or the weight of the metal scooped by the ladle is insufficient. 
Possible causes:
1. The metal pressure is too low; 3. The first stage speed is too low (the metal cools too fast in the injection cylinder); 6. The switching point of the first/second level is too late; 7. Deceleration setting error; 8. The second stage speed is too low; 14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15. Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace; 17. Blocking of the pipe of the dosing furnace; 24. Operation cycle is irregular; 28. Too little lubricating oil for the punch/stuck punch; 29. The mold is too cold; 31. Too much mold spraying; 36. Vacuum leakage; 37. The vacuum is opened too early/late; 38. Exhaust duct and/or overflow port fail; 41. The design of the inner gate and runner is poor (the part of the mold may be too cold); 42. Heat conduction control of heating and cooling points 43. It is difficult to shape the geometry of castings; 44. The metal is too hot/cold; 46. The metal specification is incorrect.
2、 Cold shut
Main features: When two streams of liquid metal meet, the interface has condensed.
Possible causes: 1. The metal pressure is too low; 3. The first stage speed is too low; 6. The switching point of the first/second stage is too late (3, 6: the metal may lose too much heat in the runner and cavity); 7. Deceleration setting error; 8. The second stage speed is too low; 14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15. Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the constant weight furnace (14, 15, 16: when pre filling is used, too much metal may cause the switching point of the first/second stage to be too late, so the metal is too cold before the second stage); 24. Operation cycle is irregular; 28. The punch lubricant is insufficient/the punch is stuck; 29. The mold is too cold; 31. Too much mold spraying; 36. Vacuum leakage; 37. The vacuum is opened too early/late; 38. Exhaust passage and/or overflow port failure (36, 37, 38: may affect the filling mode); 41. Poor design of ingate and runner:; 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points; 44. The metal is too hot/cold; 46. The metal specification is incorrect.
3、 Peeling
Main features: poor injection end point control or poor gate and runner design can produce metal delamination or oxide film.
Possible causes: 2. The metal pressure is too high (when the cavity is filled, mold expansion can cause delamination on the casting surface); 3. The first stage speed is too low; 4. The first stage speed is too high; 5. The first/second level switching point is too early; 6. The switching point of the first/second stage is too late (oxide layer may be formed during pre filling); 10. Pressurize too early; 13. The pressurization is too high; 14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15. Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace; 17. Blocking of the pipe of the dosing furnace; 23. The clamping force is too low/the machine tonnage is too small (after the cavity is filled, continue feeding to open the mold under force); 28. Too little lubricant for the punch/stuck punch (discontinuous or uneven filling of the cavity); 41. Poor design of ingate and runner (poor runner design may cause delamination during cavity filling); 47. There is scum in the molten material in the furnace.
4、 Blistering
Main features: When the mold is opened, the gas wrapped in the casting bulges towards the weak skin of the casting, which is caused by the expansion of the pressurized gas.
Possible causes: 3. The speed of the first stage is too low; 4. The first stage speed is too high (3, 4: wrong first stage speed can cause air to be brought into the metal); 5. The first/second level switching point is too early; 6. The switching point of the first/second level is too late; 14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15. Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace; 18. Setting time is too long/short; 21. Ejection delay is too short; 28. Too little lubricating oil for the punch/stuck punch (stuck punch can cause air entrainment during the first stage or speed change during cavity filling); 30. The mold is too hot; 36. Vacuum leakage; 37. The vacuum is opened too early/late; 38. Exhaust duct and/or overflow port fail; 39. Poor surface finish of mold/injection cylinder (damaged injection cylinder can be the source of air); 41. Poor design of ingate and runner; 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points; 44. The metal is too hot/cold.
5、 Flash
Main features: At the end of cavity filling, the metal pressure acting on the projected area of the casting surface is too high (shown by the pressure gauge), and the force transmitted to the parting surface is greater than the mold closing force of the machine, which opens the mold and forces the metal to flow out.
Possible causes: 2. The metal pressure is too high (check the operation window of P-Q2 curve to ensure that the pressure and projection area cannot be too high); 7. Deceleration setting error; 9. The second stage speed is too high (usually the change of the second stage speed will affect the metal pressure); 10. Pressurize too early; 13. The pressurization is too high; 19. The clamping machine/guide post is not good; 23. The clamping force is too low/the machine tonnage is too small (the pull rod may be damaged instantly or the cracks on the mold base plate may occur suddenly); 25. The mold has water/water pipe leakage (flash occurs suddenly due to similar reasons; water on the cavity surface becomes steam, which can cause serious flash); 31. Too much mold coating (the water on the cavity surface becomes steam, which can cause serious flash); 35. Dirty mold surface/metal adhesion; 39. Poor surface polishing of the mold/injection cartridge (if the mold structure and polishing are poor, the mold may not be closed tightly); 41. Poor design of ingate and runner; 44. The metal is too hot/cold (if the metal is very hot, the mold is more likely to have flash).
6、 Cold debris
Main features: The metal is cooled too much in the injection cylinder, and the resulting chill layer fragments are injected into the mold cavity. People can often see these fragments with their eyes on the casting surface.
Possible causes: 3. The speed of the first stage is too low (too low metal filling rate can increase the generation of chilling layer fragments in the pressure injection cylinder); 8. The second stage speed is too low; 15. Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace (15, 16: the source of metal fragments); 17. Blocking of the pipe of the dosing furnace; 24. Abnormal operation cycle; 29. The mold is too cold; 31. Too much mold spraying; 41. Poor design of ingate and runner; 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points; 44. The metal is too hot/cold (too cold); 46. The metal specification is incorrect (the metal composition can cause some metals to solidify in the injection cylinder at very high temperature).
7、 Oil mark
Main features: this defect occurs when too much punch oil is used.
Possible causes: 24. The operation cycle is irregular (the mold and injection cylinder may be too cold); 27. Too much punch lubricating oil; 29. The mold is too cold.
ZheJiang Dongrun Casting Industry Co,.Ltd was
built in 1995, We have been in the casting industry for more than 25
years. No matter what type of molding you need done, we are the right
supplier for your jobs. Unlike other of our competition, we offer four
types of castings.
8、 Blowhole
Main features: This defect is caused by air wrapped in the casting, which can be caused by poor injection end point control, poor gate and runner design.
Possible causes: 3. The speed of the first stage is too low; 4. The first stage speed is too high; 5. The first/second level switching point is too early; 6. The switching point of the first/second level is too late; 8. The second stage speed is too low (the percentage of solid is too high when the cavity is filled, and the second stage speed may be the cause of porosity); 11. The pressurization is too late; 12. Too low pressurization (11, 12: pressurization can be used to reduce some air holes); 14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15 Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace; 17. Blocking of the pipes of the quantitative furnace (14, 15, 16, 17: changing the volume can affect the wave acceleration and the first/second switching point); 24. Operation cycle is irregular; 28. Too little lubricating oil for the punch/stuck punch; 29. The mold is too cold (24, 29: when filling the cavity, if the mold is too cold, the air may be blocked when two strands of metal meet, which is similar to the cold compartment); 31. Too much mold spraying; 36. Vacuum leakage; 37. The vacuum is opened too early/late; 38. Exhaust passage and/or overflow port fail (36, 37, 38: air is contained in the cavity); 41. The design of the inner gate and runner is poor (for example, the gate edge of the injection cylinder and the lower ejector pin can cause air to be brought into the metal); 43. The geometric shape of the casting is difficult to form; 44. The metal is too hot/cold.
9、 Strain
Main features: insufficient draft surface inclination or side concavity causes surface damage during ejection of die casting. Changing the temperature during ejection of castings may reduce strain. Another reason is the poor surface roughness of the die.
Possible causes: 18. The solidification time is too long/short (the cooling shrinkage of the casting will cause the casting to be clamped in the mold, such as staying in the mold for a long time); 19. The clamping machine/guide post is not good; 20. The jacking force is too high; 21. Ejection delay is too short; 22. Ejection delay is too long; 30. The mold is too hot (when ejecting, the metal will be too soft, and die sticking can also occur); 32. Insufficient mold spraying; 33. Wrong mold spraying type; 34. The concentration of release agent is too low; 35. Dirty mold surface/metal adhesion (metal adhesion is a sign that the mold area is too hot, which may cause other problems, such as strain and mold adhesion); 39. Poor surface polishing of mold/injection cylinder; 40. Insufficient draft surface slope or side concave; 41. The design of the inner gate and runner is poor (cavitation and erosion can cause rapid damage to the die steel, and can also cause strain); 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points (opposite the inner gate can be a source of hot nodes); 43. The geometric shape of the casting is difficult to form; 44. The metal is too hot/cold.
10、 Hot crack
Main features: This defect is caused by solidification crack at the position with the worst tensile strength when the metal is solidified and contracted, which can be seen from the metal surface (not thermal brittleness).
Possible causes: 1. The metal pressure is too low; 7. Deceleration setting error; 8. The second stage speed is too low; 9. The second stage speed is too high; 11. The pressurization is too late; 12. The pressurization is too low; 14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15 Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace; 17. Blocking of the pipe of the constant weight furnace (15, 16, 17: when pre filling is used, the switching point of the first/second stage will change, which may cause the change of the front end of the filler at different parts of the mold); 24. The operation cycle is irregular (which may cause instability of mold temperature); 28. The punch lubricant is insufficient/the punch is stuck; 30. The mold is too hot; 32. Insufficient mold spraying; 41. Poor design of ingate and runner; 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points; 43. The geometric shape of the casting is difficult to form; 44. The metal is too hot/cold; 45. Metal is polluted or dirty; 46. The metal specification is incorrect; 47. There is scum in the molten material in the furnace.
Main features: The alloy composition remains below the high temperature zone after solidification, resulting in too weak metal. This can cause cracking in high stress areas when the casting cools (and shrinks). Note: This defect and hot crack occur at the same time.
Possible causes: 18. The solidification time is too long/short; 20. The jacking force is too high; 21. Ejection delay is too short; 22. Ejection delay is too long (18, 20, 21, 22: adjusting these parameters may solve the problem, but the root cause is not touched); 30. The mold is too hot; 32. Insufficient mold spraying; 40. Insufficient draft angle or side concave (damaged during ejection); 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points; 44. The metal is too hot/cold (which may cause overheating of some parts of the mold and overheating of some areas of the casting); 45. Metal is polluted or dirty; 46. The metal specification is incorrect (45, 46: excessive Fe, Cu and Zn can cause thermal brittleness).
12、 Depression
Main features: The depression is caused by the shrinkage cavity close to the casting surface, and is caused by the collapse of the casting surface to the shrinkage cavity during solidification. The depression is caused by poor mold temperature control, just like the shrinkage hole, because local overheating will form a depression.
Main reasons: 1. The metal pressure is too low; 7. Deceleration setting error; 8. The second stage speed is too low; 9. The second stage speed is too high; 11. The pressurization is too late; 12. The pressurization is too low (11, 12: feeding is not allowed. Sometimes feeding is not allowed because of the position of the inner gate); 14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15. Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace; 17. Blocking of the pipe of the dosing furnace; 24. Operation cycle is irregular; 26. The heating/cooling device leaks oil (in addition, the leakage of the inserted core oil cylinder can also cause oil on the surface of the mold cavity, causing depression); 30. The mold is too hot; 32. Insufficient mold spraying; 41. Poor design of ingate and runner; 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points; 43. The geometric shape of the casting is difficult to form; 44. The metal is too hot/cold; 45. Metal is polluted or dirty; 46. The metal specification is incorrect; 47. There is scum in the molten material in the furnace.
13、 Bulging
Main features: There are air
holes in the casting, which are ejected before the end of
solidification, and the trapped gas expands outward along the insecure
part to break the metal.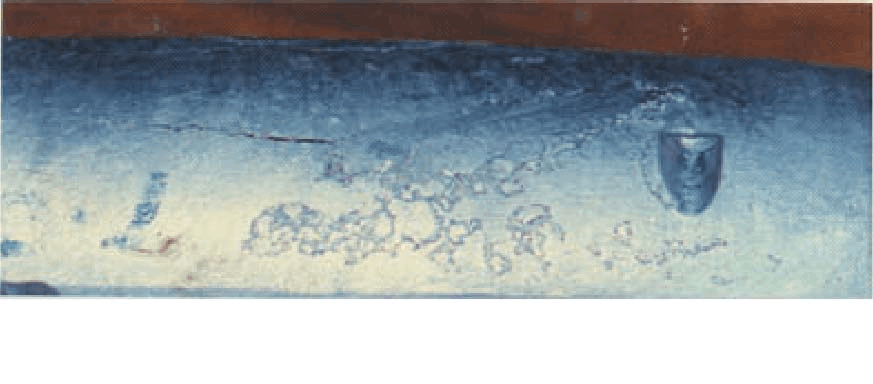
Main
reasons: 3. The speed of the first stage is too low; 4. The first stage
speed is too high; 5. The switching point of the first/second stage is
too early (3, 4, 5: the source of air intake); 14. The injection weight
of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15. Blocked at the injection port; 16.
Blocked on the launder of the constant weight furnace (14, 15, 16: the
cake is too thick and can expand); 17. Blocking of the pipe of the
dosing furnace; 18. Setting time is too long/short; 21. Ejection delay
is too short; 25. The mold has water/water pipe leakage; 26. The mold
heating/cooling oil device leaks; 27. Too much punch lubricating oil
(25, 26, 27: the source of gas entrapment); 30. The mold is too hot; 32.
Insufficient mold spraying; 36. Vacuum leakage; 37. The vacuum is
opened too early/late; 38. Exhaust duct and/or overflow port fail; 41.
Poor design of ingate and runner; 42. Poor heat conduction control of
heating and cooling points; 43. It is difficult to shape the geometric
shape of the casting (mostly at the wall thickness); 44. The metal is
too hot/cold;
14、 Bending
Main features:
after casting ejection, deformation will occur when the casting is
cooled to room temperature. The root cause is caused by some geometric
shape or alloy composition of the casting. Reducing the ejection
temperature can minimize the deformation. Uneven die temperature is one
of the main reasons for this defect.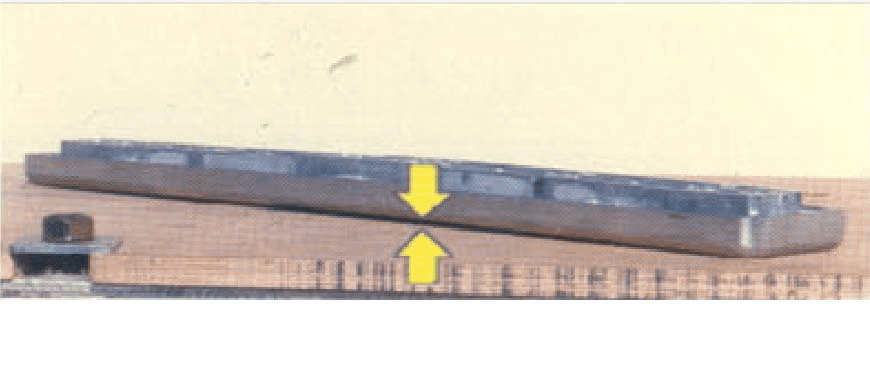
Main
reasons: 18. The solidification time is too long/short; 21. Ejection
delay is too short; 22. Ejection delay is too long; 24. Operation cycle
is irregular (poor temperature control); 30. The mold is too hot; 32.
Insufficient mold spraying; 33. Wrong mold spraying type; 34. The
concentration of release agent is too low; 40. Insufficient draft
surface slope or side concave; 41. Poor design of ingate and runner; 42.
Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points (poor
filling mode may centralize the heat load in some areas of the mold);
43. The geometric shape of the casting is difficult to form; 44. The
metal is too hot/cold; 46. The metal specification is incorrect.
15、 Die gluing
Main
features: chemical impact and adhesive force of aluminum alloy on die
steel, which will cause the casting to be torn during ejection. Changing
the alloy composition and reducing the temperature of metal or die can
reduce die sticking.
Main
reasons: 2. The metal pressure is too high; 5. The switching point of
the first/second stage is too early (pre filling can sometimes help
reduce die sticking in some areas); 9. The second stage speed is too
high (in some instances, changing the metal speed can increase the heat
transfer to the problem area); 15. Blocked at the injection port; 16.
Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace; 17. Blocking of
the pipes of the quantitative furnace (15, 16, 17: the change of the
volume will change the actual first/second stage switching point. This
can change the heat distribution state of the mold); 30. The mold is too
hot; 32. Insufficient mold spraying; 33. Wrong mold spraying type; 34.
The concentration of release agent is too low; 39. Poor surface
polishing of the mold/injection cylinder (the mold may need polishing);
41. Poor design of ingate and runner; 42. Poor heat conduction control
of heating and cooling points; 44. The metal is too hot/cold; 46. The
metal specification is incorrect (when Fe is lower than the standard of
0.6-0.7%, it may cause die sticking).
Dongrun Casting have 20000 square meters facility houses and 200 production & test equipment, From quotation and tooling design to casting and finished machining, we can work with you at every stage. We serves wide range of industries-from Fortune 500 corporations to small and midsize OEMs. Our products includes:
❖ HVAC | ❖ Architectural parts |
16、 Shrinkage cavity
Main
features: This defect is caused by the metal volume becoming smaller
during solidification, and the metal has no more metal to feed before
solidification. Local overheating can concentrate shrinkage cavities in
specific areas, see "Sags".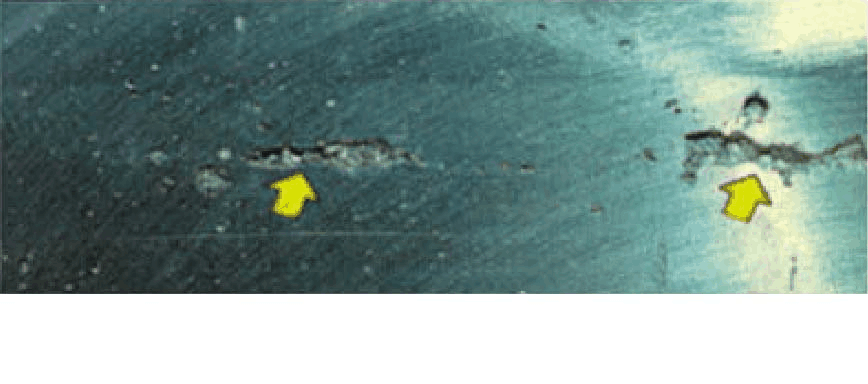
Main
reasons: 1. The metal pressure is too low; 7. Deceleration setting
error; 8. The second stage speed is too low; 9. The second stage speed
is too high; 11. The pressurization is too late; 12. The pressurization
is too low; 14. The injection weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15
Blocked at the injection port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the
quantitative furnace; 17. The pipe of the constant weight furnace is
blocked (14, 15, 16, 17: when the pressure is increased, shrinkage
cavity can occur when the cake is too thin); 24. Abnormal operation
cycle; 28. The punch lubricant is insufficient/the punch is stuck; 30.
The mold is too hot; 32. Insufficient mold spraying; 41. Poor design of
ingate and runner (improving the design of ingate and runner can improve
the feeding in some areas); 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating
and cooling points; 43. The geometric shape of the casting is difficult
to form; 44. The metal is too hot/cold; 45. Metal is polluted or dirty
(shrinkage cavity is related to oxide and slag); 46. The metal
specification is incorrect; 47. There is scum in the molten material in
the furnace.
17、 Analysis of Defects in Hot Lattice Die Casting
Main
features: This defect is caused by the continuous expansion and
contraction of the die steel surface during use. Excessive cold die and
die fatigue will accelerate this result.
Main
reasons: 2. The metal pressure is too high; 7. Deceleration setting
error; 13. The pressurization is too high; 24. The operation cycle is
irregular (the mold is too cold); 29. The mold is too cold; 30. The mold
is too hot; 31. Too much mold spraying; 41. Poor design of ingate and
runner; 42. Poor heat conduction control of heating and cooling points;
43. The geometric shape of the casting is difficult to form; 44. The
metal is too hot/cold;
18、 Analysis of Leakage Die Casting Defects
Main
features: The reason for casting leakage is that there are oxides
overlapping or connecting there, or there are multiple holes connecting
to form a leak path. Careful inspection of the leak area can reveal many
causes of the leak.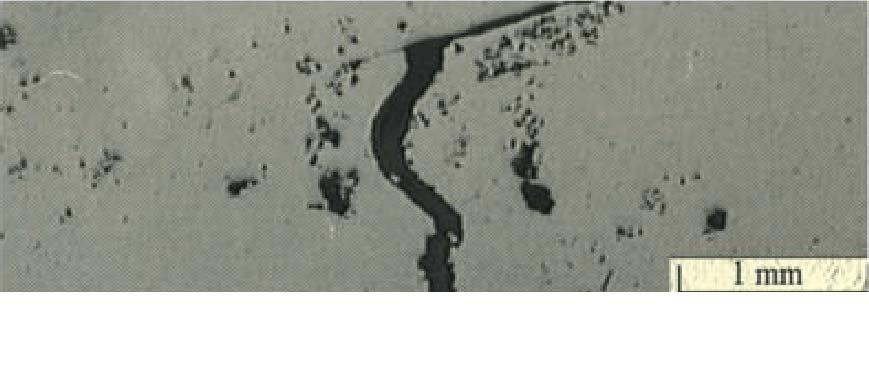
Main
reasons: 1. The metal pressure is too low; 3. The first stage speed is
too low; 4. The first stage speed is too high; 5. The first/second level
switching point is too early; 6. The switching point of the first
stage/the second stage is too late (during the pre filling, the
solidified metal in the runner, ingate and cavity can destroy the
filling mode, and the generated chill layer fragments can also cause
leakage); 7. Deceleration setting error; 8. The second stage speed is
too low; 11. The pressurization is too late; 12. Too low pressurization
(the pressure of the machine accumulator may be low or the
pressurization circuit does not work effectively); 14. The injection
weight of the spoon is set incorrectly; 15. Blocked at the injection
port; 16. Blocked on the flow channel of the quantitative furnace; 17.
Blocking of the pipes of the constant weight furnace (14, 15, 16, 17:
the deviation of the first/second stage switching point that affects the
metal in the runner and mold cavity, and the first/second stage
switching point may be the reason that the air is wrapped before the
injection cylinder is filled); 25. The mold has water/water pipe
leakage; 26. The mold heating/cooling oil device leaks; 27. Too much
punch lubricating oil; 28. The punch lubricant is insufficient/the punch
is stuck; 29. The mold is too cold; 30. The mold is too hot; 31. Too
much mold coating (25, 26, 27, 28, 30, 31: the source of porosity); 36.
Vacuum leakage; 37. The vacuum is opened too early/late; 38. Exhaust
duct and/or overflow port fail; 39. Poor surface polishing of
mold/injection cylinder; 41. Poor design of ingate and runner; 42. Poor
heat conduction control of heating and cooling points; 43. The geometric
shape of the casting is difficult to form; 44. The metal is too
hot/cold; 45. Metal is polluted or dirty; 46. The metal specification is
incorrect; 47. There is scum in the molten material in the furnace (45,
46, 47: changing the metal composition or specification can improve its
pressure tightness).
ZheJiang Dongrun Casting Industry Co,.Ltd was built in 1995, We have been in the casting industry for more than 25 years. No matter what type of molding you need done, we are the right supplier for your jobs. Unlike other of our competition, we offer four types of castings.
Dongrun Casting have 20000 square meters facility houses and 200 production & test equipment, From quotation and tooling design to casting and finished machining, we can work with you at every stage. We serves wide range of industries-from Fortune 500 corporations to small and midsize OEMs. Our products includes:
❖ HVAC | ❖ Architectural parts |
Browse our online showroom to see what we can do for you. And then E-mail:dongrun@dongruncasting.com us your specifications or inquiries today
